TEFAL JAMIE OLIVER E3040444 Cook's Direct SS Stekpanna Rostfritt Stål 24 Cm Stekpanna 20 24 & 28 Cm Thermo-Signal Mycket Slitstark & Lätt Att Rengöra : Amazon.se: Hem & kök

Le Creuset ~ Enameled Cast Iron ~ Marseille ~ 11.75" Signature Iron Handle Skillet, Price $250.00 in Pittsburgh, PA from Contemporary Concepts
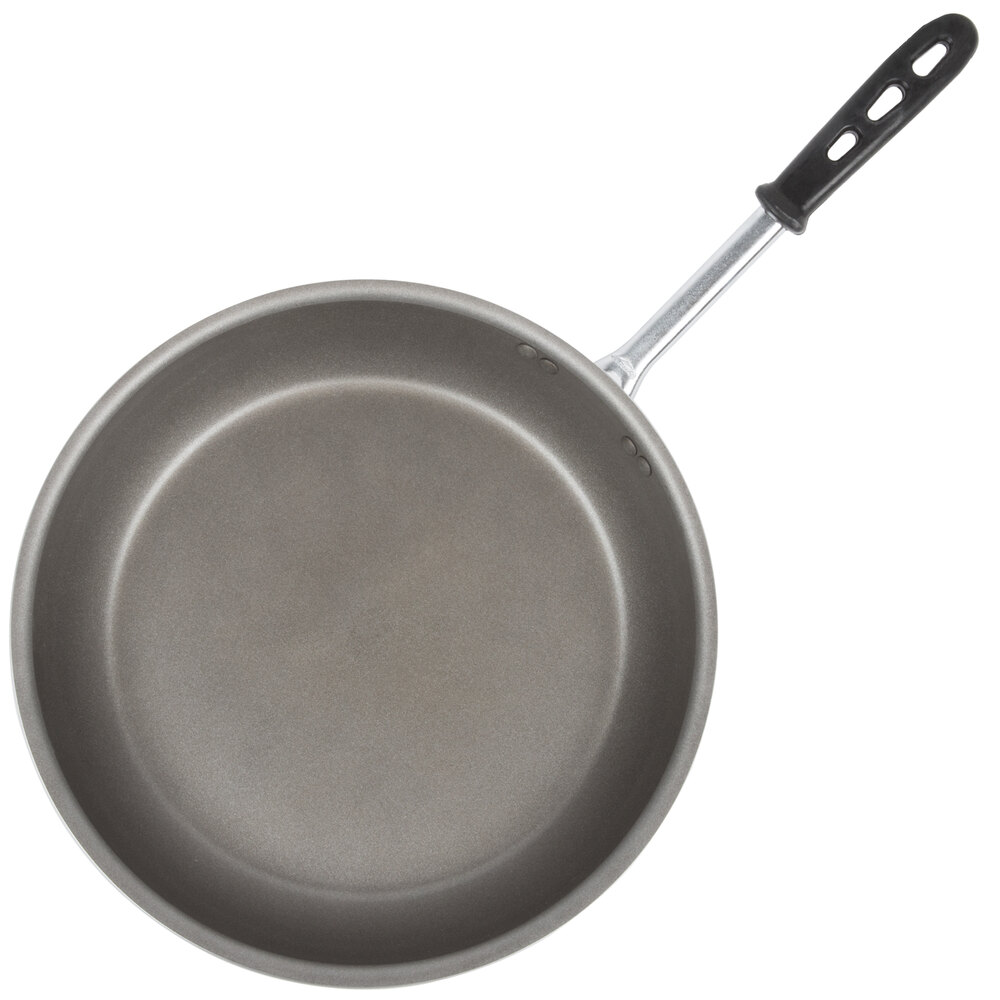

Vollrath 67814 Wear-Ever 14" Aluminum Non-Stick Fry Pan with PowerCoat2 Coating and Black TriVent Silicone Handle

toolab.se | Maskiner, Verktyg & Kläder på nätet & butikToolab | Maskiner & verktyg på nätetMuurikka Stekpanna utan skaft | toolab.se